How to find circular references in Excel, when the software alerts you to their presence but not always their location? In a large file, it can take a lot of time to find the source of the problem. PerfectXL saves you this effort by showing you the exact path of the circular reference and helping you identify and resolve the issue.
- Download the sample file to follow the steps.
- Already working with PerfectXL? Then jump to the solution with PerfectXL.
Step-by-step without PerfectXL
That dreadful pop-up
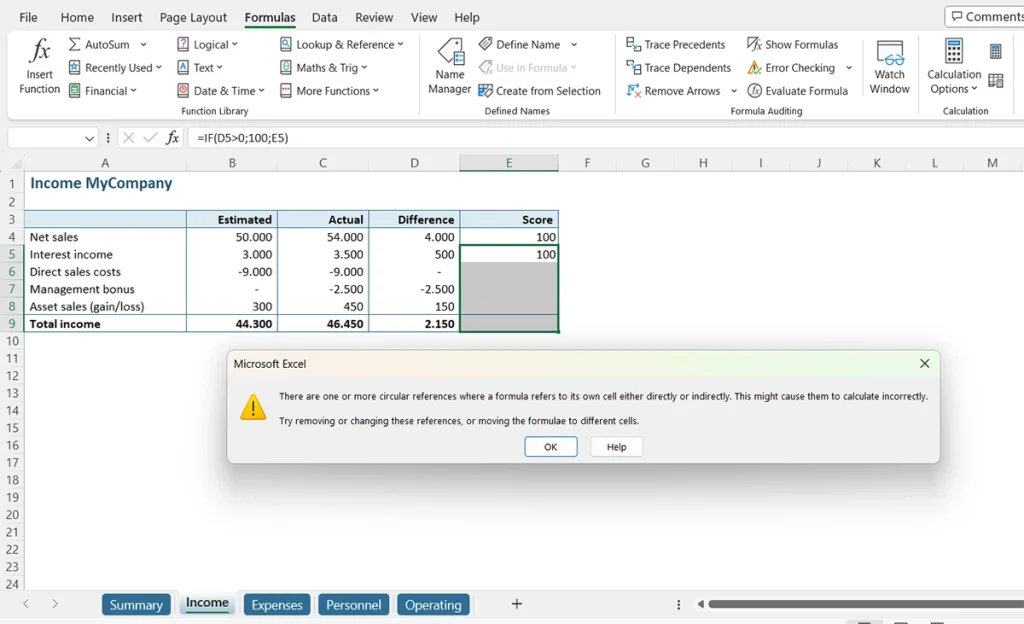
When your file contains a circular reference, that dreadful – familiar to many Excel users – popup will appear after opening it:
But what in case of hidden circular references?
Sometimes circular references are hidden. This is the case when a reference is only circular under certain conditions.
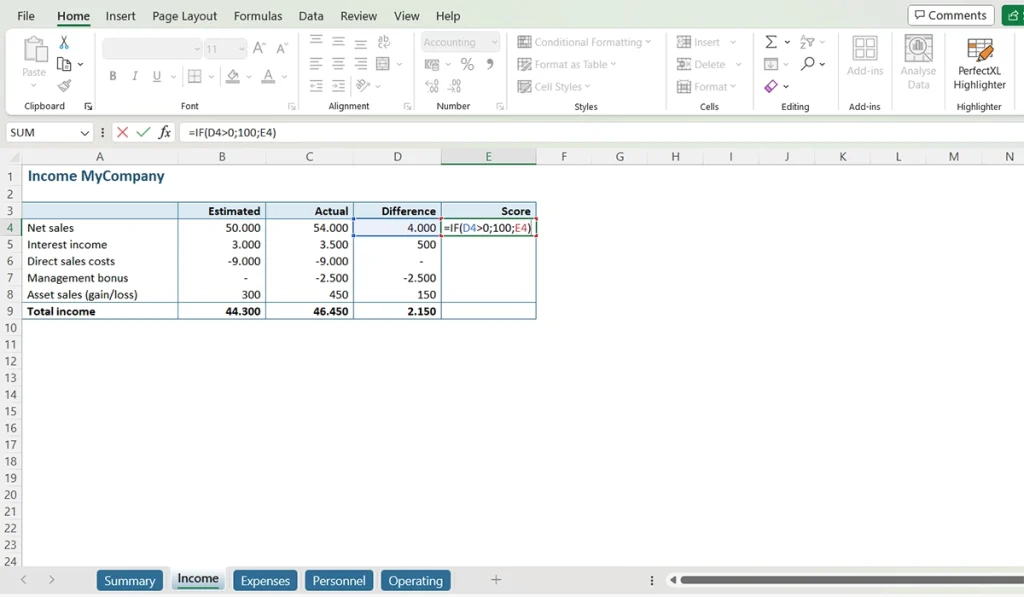
As a simple example, let’s add a “Score” column to the “Income” tab of our sample file. Every time more is received than originally estimated, we assign a score of 100 to the Score column. We note this formula as follows:
=IF (D4 > 0; 100; E4)
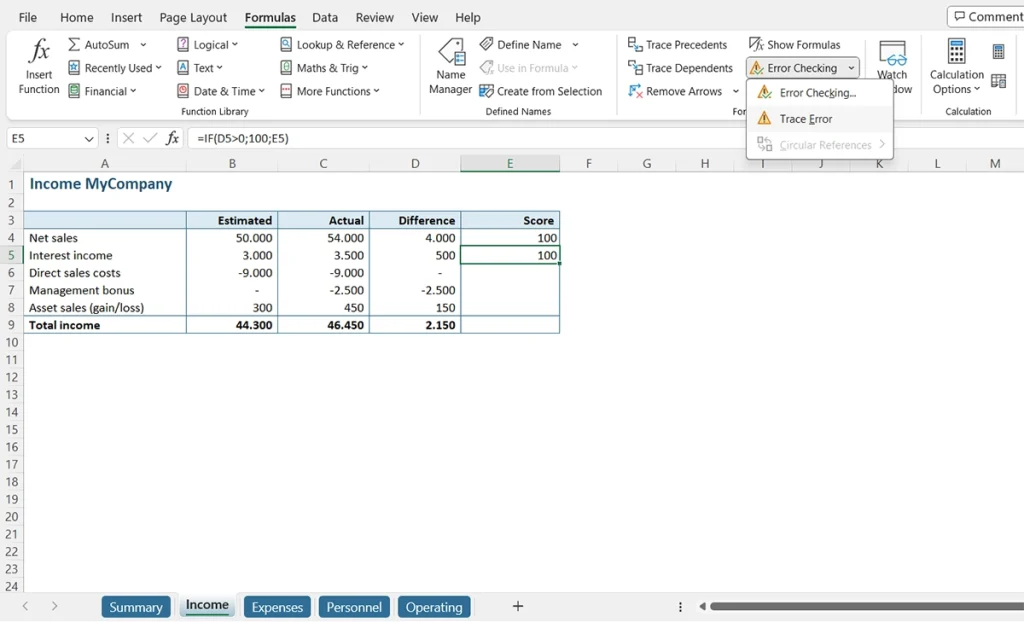
In essence, we say here: as long as the number in cell D4 is greater than zero, then the value of cell E4 will be “100”, but when the number in cell D4 is less than or equal to zero, then the value of cell E4 is the value of E4 (no wonder Excel is confused). The circular reference is only apparent in the second case. Look, when we drag the formula to row 5, there’s no apparent issue because the value in cell D5 is also greater than zero.
Conclusion
In the above example, you clearly see that circular references can depend on variables and thus pose a risk. Moreover, it is a simple example; in more extensive spreadsheets with complex formulas, discovering circular references can be a challenging task.
Step-by-step with PerfectXL
Step 1: Check for circular references from the Excel ribbon
Circular references can be incredibly frustrating, particularly when Excel notifies you of their presence but doesn’t pinpoint their exact location. Before you start ripping your hair out, try PerfectXL Risk Finder. After installation, open the file you want to inspect in Excel and navigate to the PerfectXL in the Excel menu bar. In the PerfectXL ribbon, under “Detect Problems” select “Circular References.”
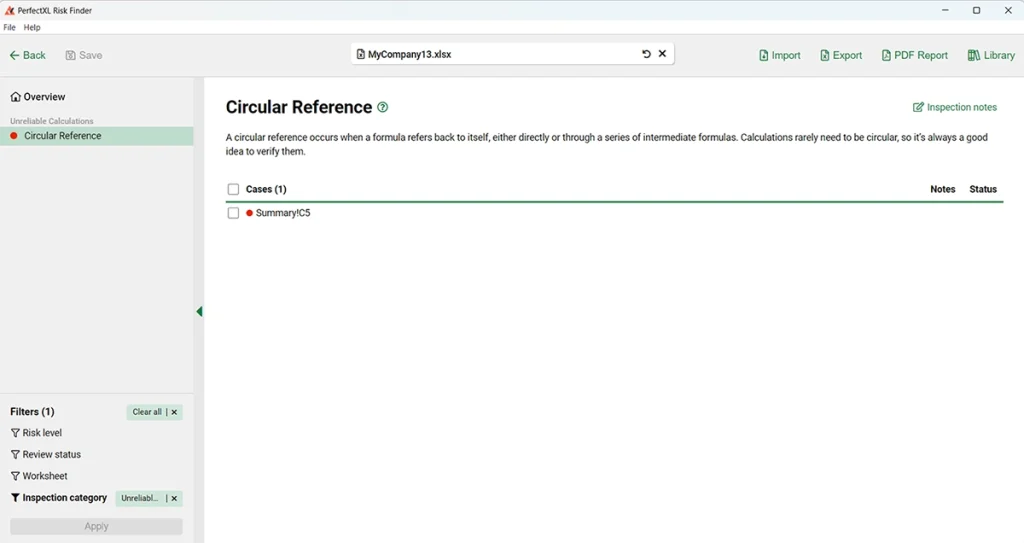
Step 2: Analyze a file in PerfectXL Risk Finder
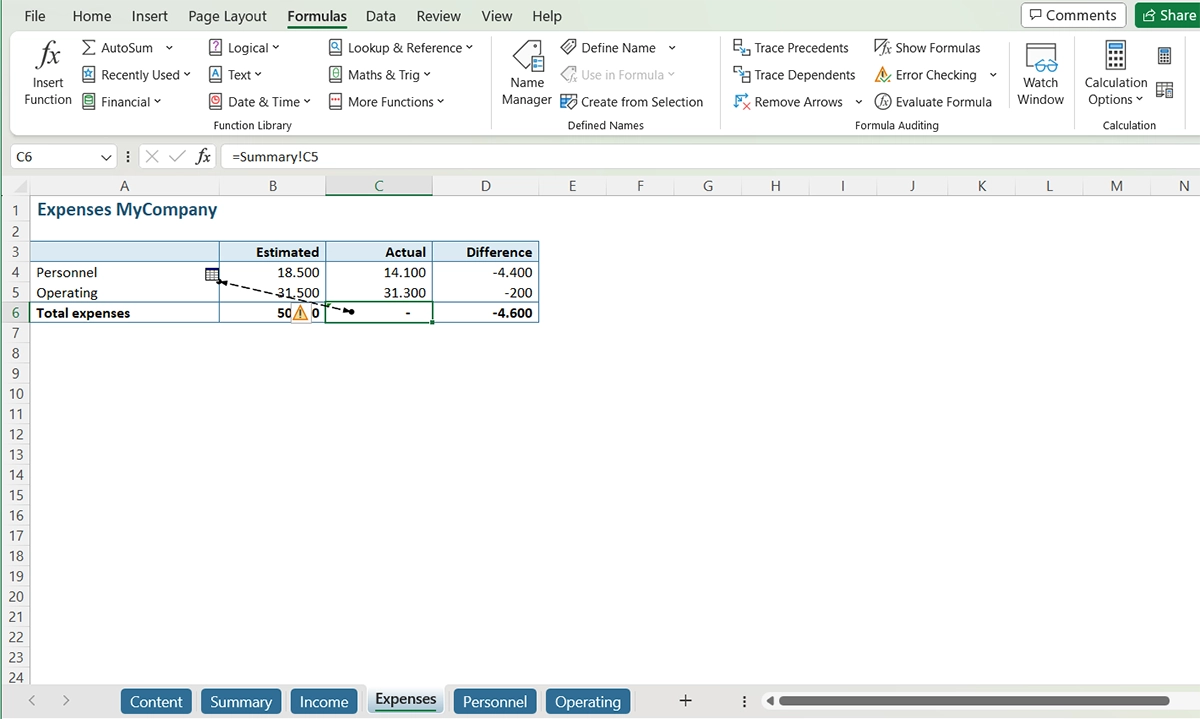
PerfectXL Risk Finder will automatically analyze your file and open an overview of circular references found (in this case only one).
To get more information about a finding (like where it’s located, what it looks like and how to fix it), just click on it (in this case “Summary!C5”).
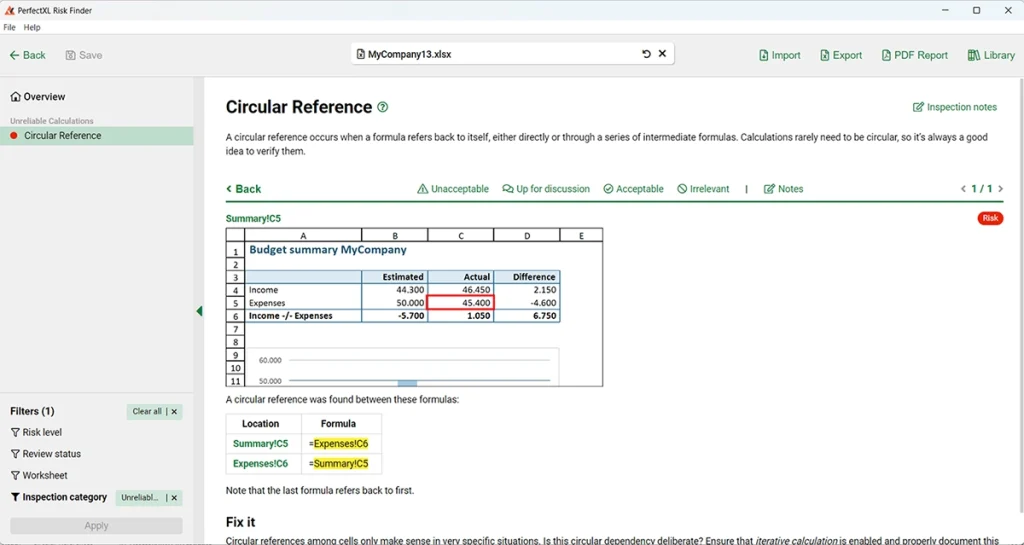
Step 3: Inspect the details of a circular reference
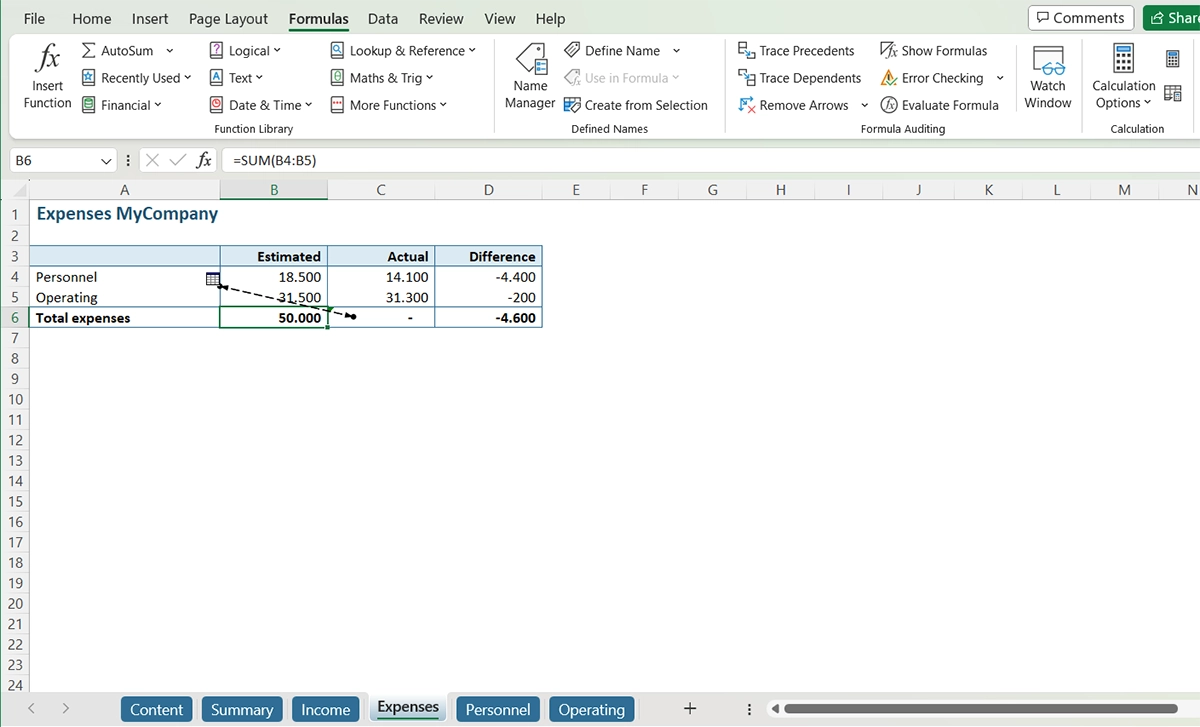
Here you’ll find a clear image of the context of the circular reference: a screenshot of the location and a table containing all cells involved (the highlights will show you which references are causing the circularity). In this case, it’s a simple two cell circularity in which both cells refer to each other. PerfectXL Risk Finder is also capable of identifying circular references in complex formula chains.
From this screen you can navigate directly to the location in your Excel file by either clicking on the screenshot or selecting a cell reference from the table to jump to that location. Let’s try from the screenshot.
Step 4: Resolve the issue
In this case, due to the simplicity of our example, it’s easy to see what is happening and how to resolve the issue. As the table showed us in the previous PerfectXL Risk Finder screenshot, there is a simple matter of a cross-reference and adjusting one or both cells involved will make the model function properly again.
Conclusion
PerfectXL Risk Finder helps you locate both visible and hidden circular references within your file, even when the option ‘Iterative Calculation’ is enabled. It offers transparent insights into their structures, making it a straightforward task to resolve them. The verification of circular references in your file before sharing it with colleagues or clients ensures a seamless experience without unexpected issues down the road.